Blockchain scalability remains a pivotal challenge, prompting the exploration of innovative blockchain scalability solutions like Plasma and sharding.
As decentralized networks continue to evolve, the need to process transactions more efficiently and accommodate growing user demands has become increasingly pressing. Both Plasma and sharding offer distinctive approaches to address this fundamental challenge, aiming to optimize transaction throughput and overall network performance.
In this guide, we explore the intricacies of these two strategies, uncovering their unique features, benefits, and potential drawbacks. By examining the core principles, mechanisms, and real-world implications of each approach, we gain a comprehensive understanding of how these technologies shape the landscape of blockchain scalability. Join us as we unravel the complexities of these competing solutions and shed light on their contributions to the future of decentralized systems.
What is Plasma?
Plasma, commonly known as Ethereum Plasma because it was first proposed by Ethereum co-founder Vitalik Buterin, is a scaling solution aimed at enhancing the performance of the Ethereum network. Its core premise revolves around establishing a network of side chains that maintain minimal interaction with the Ethereum blockchain, commonly referred to as the main chain. The foundational structure of Plasma adopts a hierarchical arrangement resembling a blockchain tree, wherein multiple “child chains” are layered atop the primary chain.
Illustration of plasma blockchain. Source: ResearchGate
The Plasma framework empowers the creation of an extensive array of side chains (also called child chains), essentially acting as condensed replicas of the Ethereum blockchain through the utilization of smart contracts and Merkle Trees.
These side chains are uniquely designed to execute customized smart contracts, accommodating diverse requirements of various entities. This adaptability enables the creation of distinct Plasma smart contracts tailored to specific use cases, thereby allowing companies to harness the potential of the Plasma framework to meet their individual needs.
By capitalizing on the security provided by the main chain, Plasma facilitates the deployment of numerous child chains. These chains operate independently, adhering to predetermined guidelines and pursuing specific objectives that may not necessarily align with those of the main chain. This design strategy aims to alleviate congestion concerns within the primary Ethereum blockchain.
Components of Ethereum Plasma
To grasp the mechanics of Ethereum Plasma, it’s vital to explore the foundational components that underpin this network:
1. Off-Chain Computation
The concept of off-chain computation establishes a sense of trust within the Ethereum network participants. It facilitates the settlement of multiple transactions outside the primary Ethereum blockchain. This principle stems from the notion that not every transaction necessitates validation from all nodes on the main chain.
Consequently, this selective transaction validation eases the workload on the primary chain, alleviating congestion and enhancing efficiency. Developers meticulously structure Plasma blockchains, often employing a single operator to expedite transaction processing, resulting in swifter and cost-effective transactions.
2. State Commitments
Ethereum Plasma adopts the practice of periodically publishing state commitments on the Ethereum mainnet. This synchronization ensures mutual awareness of the child chains’ state and maintains compatibility between them.
This interplay is vital for Plasma’s ability to leverage the security of the main chain. While transactions occur off-chain, final settlements transpire within the primary Ethereum execution layer. This interlocking relationship prevents inconsistencies and safeguards against the proliferation of invalid transactions.
3. Entries and Exits
Seamless interaction between both blockchains is a fundamental prerequisite when amalgamating the Ethereum main chain with Plasma.
This necessitates establishing a communication channel that facilitates asset transfer, thus realizing the scalability solution. Plasma executes this via a master contract on Ethereum, orchestrating the mechanics of entries and exits.
4. Dispute Arbitration
Dispute resolution stands as a pivotal facet of Ethereum Plasma’s scalability design. A mechanism rooted in transaction integrity enforcement is employed to counter the possibility of malicious actions by participants.
This safeguard, known as Fraud Proof, is devised to identify participants engaging in suspicious behavior. Fraud proofs serve as claims contesting the validity of specific state transitions.
Users invoke them when detecting potential double-spends, where an asset is attempted to be spent twice before confirmation completion. Vigilance and prompt reporting are key to the effectiveness of this process. Users who promptly publish fraud proofs halt illicit transactions, leading to punitive action against culprits.
How Does Ethereum Plasma Work?
In essence, Plasma represents an off-main-chain solution strategically designed to significantly enhance the operational efficiency of the Ethereum network and analogous blockchains. This optimization is achieved by offloading a substantial portion of processing tasks from the main chain onto a network of smaller, specialized chains, each serving distinct functions.
Although Plasma transactions are executed off-chain, they are settled on the main Ethereum execution layer to ensure security guarantees. However, finalizing off-chain transactions requires periodic publication of “state commitments” by the operator, responsible for generating plasma chain blocks. These commitments, resembling Merkle roots derived from Merkle trees, are cryptographic ways of committing to values without revealing them. They prevent altering committed values and play a pivotal role in upholding security.
Merkle roots are cryptographic constructs that enable condensing large data amounts. These roots, also termed “block roots,” can represent entire block transactions, aiding in confirming small data’s inclusion within a broader dataset. Users can validate data inclusion using Merkle proofs, especially to demonstrate transaction presence in a specific block.
Merkle roots serve a vital purpose by conveying off-chain state data to Ethereum. Analogously, they function as “save points,” where the operator signifies the Plasma chain’s state at a specific time and corroborates it with a Merkle root as evidence. This act of committing to the ongoing plasma chain state using a Merkle root is termed a “state commitment.”
Although originally conceptualized by Vitalik Buterin and Joseph Poon in August 2017 to address Ethereum’s scalability challenges, the Plasma concept exhibits adaptability for integration into other blockchain platforms. Joseph Poon, a proponent of the Lightning Network proposal for Bitcoin, is instrumental in highlighting the synergies between Plasma and Lightning Network as scalability solutions for their respective blockchains. It is important to note that while these solutions share common goals, they employ distinct methodologies and mechanisms.
The Ethereum Plasma project remains an open-source initiative, with its code repository accessible on GitHub. For a deeper dive into the technical intricacies, the official Plasma whitepaper serves as a valuable resource. Despite being in the nascent stages of development, the concept of Plasma holds immense promise. Successful implementation has the potential to usher in a new era of efficiency for the Ethereum network, while also serving as a foundational template for other blockchain networks seeking scalability solutions.
Benefits of using Plasma for blockchain scalability
- Plasma chains offer a distinct advantage over channels by enabling asset or coin transfers to any recipient, as opposed to channel transactions limited to bilateral parties.
- Plasma chains exhibit a key edge over sidechains due to their anchoring within the security of the mainchain. While a sidechain breach leaves the mainchain unaffected, it can’t safeguard users on the sidechain. In contrast, plasma chains harness mainchain security, empowering users to exit to the mainchain if the plasma chain faces threats. This dynamic grants plasma superior security compared to sidechains.
Limitations of using Plasma for blockchain scalability
- An inherent limitation of plasma is the protracted withdrawal timeline for users aiming to shift their coins from layer 2 to layer 1.
- Users are subject to a waiting period of 7–14 days for withdrawals, essential for scrutinizing the withdrawal transaction’s legitimacy and preventing fraudulent activity.
What is Sharding?
Sharding is a technique that involves dividing blockchains or databases into smaller, partitioned sections called shards, each managing specific data segments. This alleviates the strain on a single chain processing all network transactions. Shards function as individual blockchains, capable of handling their transactions, while a main chain or beacon chain oversees shard interactions. This Layer 1 network upgrade enhances scalability by distributing the workload. Ethereum was among the first blockchains to adopt sharding as it started its transition to a scalable Proof of Stake network, with a Beacon Chain coordinating multiple shards.
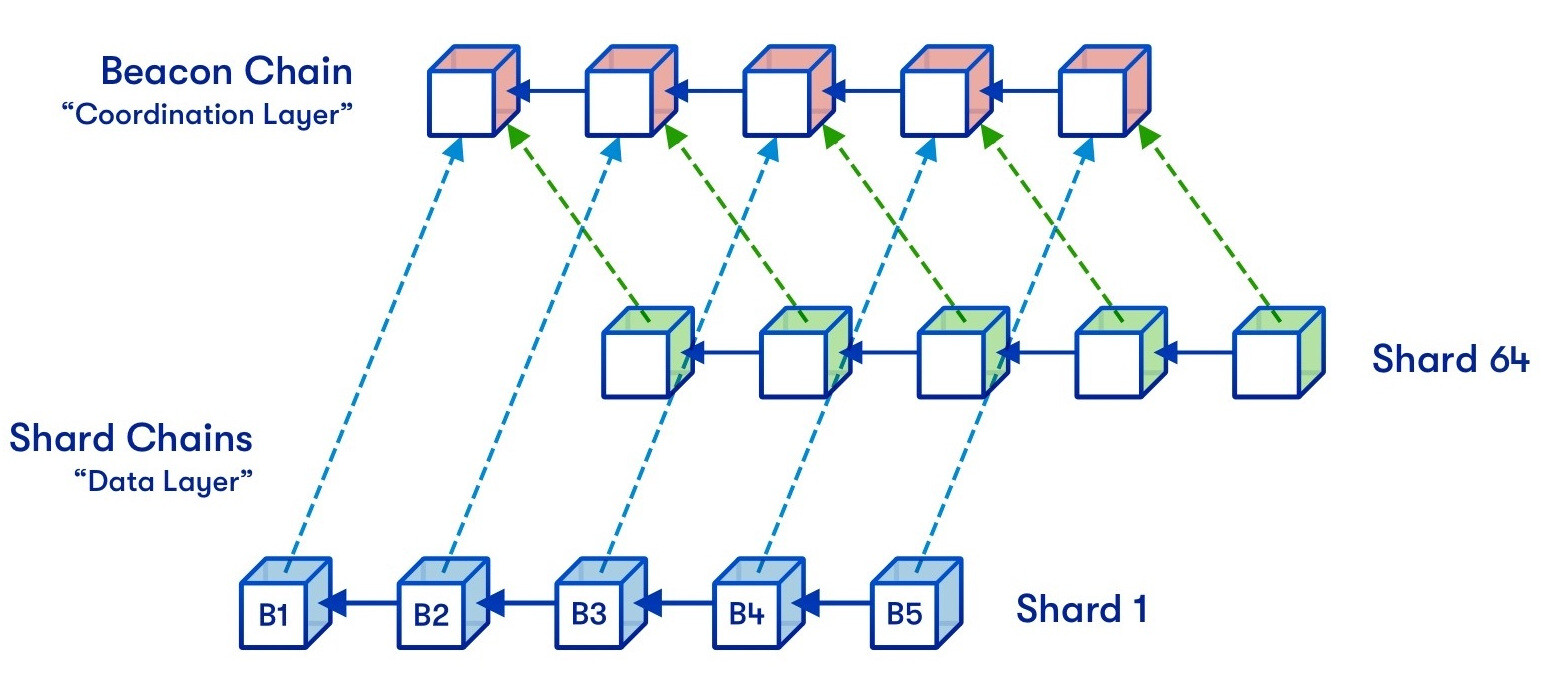
Illustration of Ethereum sharding. Source: vitalik.eth.limo
A significant advantage of sharding is simplified node operation. As data is divided across shards, validator nodes no longer need to store the entire blockchain history, focusing only on data integrity confirmations. Sharded networks complement rollups, which improve scalability by validating off-chain transactions and consolidating them on the main chain. Sharding enhances rollup efficiency by allowing them to report states more swiftly.
However, sharding introduces security concerns. A malicious actor gaining control of a shard could potentially disrupt other parts of the network. Proper regulations and safeguards are necessary to prevent this issue, as taking over a shard is comparatively easier than hijacking an entire non-sharded network.
How Does Sharding Work?
Sharding plays a pivotal role in achieving efficient data storage distribution, leading to enhanced cost-effectiveness in rollups and simplified node operations. This approach empowers layer 2 solutions to leverage Ethereum’s security while concurrently maintaining lower transaction fees.
The Ethereum blockchain currently hosts over three thousand decentralized applications (dApps), underscoring the pressing need for scalability solutions like sharding.
Sharding entails the division of the network into smaller units or partitions, each of which substantially boosts the network’s Transactions Per Second (TPS).
However, while sharding may appear straightforward, it involves several crucial components and intricacies:
1. Nodes
Nodes within a blockchain network handle the processing and management of all transaction volumes occurring within the network. These autonomous entities are tasked with preserving and storing decentralized network-generated data, including account balances and transaction histories. Nodes manage all activities, data, and transactions within the network, a design decision that has persisted since network inception.
However, this design hampers transaction processing speed, even though it maintains blockchain security by storing every transaction on each node. This sluggish transaction processing stands as a hindrance to a future where blockchains are expected to manage millions of transactions.
2. Horizontal Partitioning
Sharding can be achieved through the horizontal partitioning of databases, wherein rows are divided into segments or shards based on their characteristics.
For instance, one shard could focus on storing transaction history and the current state of a specific category of addresses. Shards might also be categorized by the type of digital asset they contain, allowing for specialized transaction handling involving those assets.
Benefits of blockchain Sharding
The processing capacity of blockchain networks is constrained due to the necessity for all nodes to reach consensus on transaction legitimacy before processing. This requirement maintains the decentralized nature of networks like Ethereum and Bitcoin, wherein every node retains the entire blockchain history and processes each transaction.
1. Data Security and Compression
This design fortifies network security against hostile takeovers or transaction alterations, even though it hampers scalability. Sharded blockchains introduce an alternative by allowing nodes to forgo downloading the full history or validating every transaction. This bolsters network performance, enhancing its ability to accommodate more users.
2. Enhanced Scalability
Sharding’s foremost benefit is the scalability boost it affords blockchains. Sharding permits the integration of additional nodes and larger data sets without significantly slowing down transaction speeds. This holds potential for expediting the adoption of blockchain technology across industries, particularly in finance, where quicker transactions can foster competition against centralized payment systems.
3. Improved Accessibility
Sharding brings two supplementary advantages: heightened network participation and improved user accessibility. Anticipated enhancements in Ethereum’s sharding may reduce the hardware prerequisites for running a client, enabling participation from personal computers and mobile devices. This democratization of access can broaden network participation.
Security Considerations in Sharding
It’s important to note that sharding’s application to blockchain networks is in the preliminary testing phase. It is mostly associated with the following risks:
1. Risk of Shard Collisions
One security concern pertains to shard collisions, where one shard takes over another or overrides its data. This risk could lead to data loss or the introduction of corrupted data by malicious shards. Ethereum 2 mitigates this risk by randomly assigning nodes to shards and reassigning them at intervals.
2. Risk of Shard Corruption
Considering each shard as an independent blockchain network with its users and data reveals a potential risk—shard corruption. An attacker gaining control of a shard could introduce fraudulent transactions. Ethereum addresses this through random shard assignment and reassignment, thwarting attackers’ ability to predict and exploit vulnerabilities.
Conclusion
Plasma, pioneered by Vitalik Buterin and Joseph Poon, introduces side chains that interact with the main chain minimally. This architecture enables the creation of numerous child chains with customized smart contracts, easing congestion on the primary chain while maintaining security.
In contrast, sharding focuses on partitioning the network into smaller, manageable segments known as shards. Each shard processes specific transactions, alleviating strain on a single chain and bolstering scalability.
While both Plasma and sharding share the goal of scalability, they possess distinctive mechanisms. Plasma emphasizes side chains, diversifying use cases, while sharding focuses on segmenting the main chain for increased efficiency. Their ongoing development is set to reshape blockchain’s potential, offering alternatives to tackle scalability challenges.
Updated in September 2025.

