[ad_1]
In the early 2020s, quantum computing hit the public spotlight as a potential threat to Bitcoin. Relying on SHA-256 cryptographic hash function for its proof-of-work network consensus, Bitcoin’s value is predicated on computational power.
If there is a technology that can circumvent the traditional binary system of 0s and 1s for units of information, there is potential to upend cryptography as we know it. But is that danger over exaggerated?
Could quantum computing one day turn Bitcoin into a valueless piece of code? Let’s start by understanding why Bitcoin relies on cryptography.
Bitcoin’s Bits and Hashing
When we say that an image is 1 MB in size, we say that it contains 1,000,000 Bytes. As each Byte contains 8 bits, this means that an image contains 8,388,608 bits. As the binary digit (bit), this is the tiniest unit of information, either 0 or 1, that builds up the entire edifice of our digital age.
In the case of an image, bits in a 1MB file would assign a color to each pixel, making it readable to the human eye. In the case of a cryptographic function like SHA-256 (Secure Hash Algorithm 256-bit), developed by the NSA, it would produce 256 bits (32 Bytes) as the fixed length of a hash from an input of arbitrary size.
The primary purpose of a hash function is to convert any string of letters or numbers into an output of fixed length. This obfuscation blending makes it ideal for compact storage and anonymized signatures. And because the hashing process is a one-way street, hashed data is effectively irreversible.
Therefore, when we say that SHA-256 provides a 256-bit security, we mean to say that there are 2256 possible hashes to consider for reversal. When Bitcoin payments are conducted, each Bitcoin block has its own unique transaction hash generated by SHA-256. Each transaction within the block contributes to this unique hash as they form the Merkle root, plus the timestamp, nonce value and other metadata.
A would-be blockchain attacker would have to recalculate hashes and extract the necessary data not only for that block containing the transactions, but for all subsequent blocks chained to it. Suffice to say, the 2256 possibility load poses a virtually impractical computational endeavor, requiring immense expenditure of energy and time, both of which are exceedingly costly.
But could this no longer be the case with quantum computing?
New Quantum Paradigm for Computing
Moving away from bits as 0s and 1s, quantum computing introduces qubits. Leveraging the observed property of superposition, these units of information can not only be either 0 or 1 but both simultaneously. In other words, we are moving away from deterministic computing to indeterministic computing.
Because qubits can exist in an entangled and superimposed state, until observed, computations become probabilistic. And because there are more states than always 0 or 1, a quantum computer has the ability for parallel computing as it can simultaneously process 2n states.
A classic binary computer would have to run a function for each possible 2n state, which the quantum computer could assess simultaneously. In 1994, mathematician Peter Shor developed an algorithm with this in mind.
Shor’s algorithm combines Quantum Fourier Transform (QFT) and Quantum Phase Estimation (QPE) techniques to speedup pattern-finding and theoretically break all cryptography systems, not just Bitcoin.
However, there is one huge problem. If quantum computing is probabilistic, how reliable is it?
Stabilizing Coherence in Quantum Computing
When it is said that qubits are superimposed, this is akin to visualizing a coin flip. While in the air, one can imagine the coin having both states – heads or tails. But once it lands, the state is resolved into one outcome.
Equally so, when qubits are resolved, their state collapses into the classical state. The problem is that a ground-breaking algorithm like Shor’s needs many qubits to maintain their superposition for a long period of time to interact with each other. Otherwise, the necessary, useful calculations fail to actually complete.
In quantum computing, this refers to quantum decoherence (QD) and quantum error correction (QEC). Moreover, these problems need to be solved across many qubits for complex calculations.
According to the Millisecond Coherence in a Superconducting Qubit paper published in June 2023, the longest coherence time of a qubit is 1.48 ms at average gate fidelity of 99.991%. The latter percentage refers to the overall reliability of a QPU (quantum processing unit).
At present, the most usable and powerful quantum computer appears to be from IBM, dubbed Quantum System Two. A modular system ready for scaling, Quantum System Two should perform 5,000 operations with three Heron QPUs in a single circuit by the end of 2024. By the end of 2033, this should increase to 100 million operations.
The question is, would this be enough to materialize Shar’s algorithm and break Bitcoin?
QC Threat Viability
Due to decoherence problems and fault-tolerance, quantum computers have yet to pose a serious risk to cryptography. It is unclear if it is even possible to achieve a fault-tolerant quantum system at scale when such a high level of environmental purity is needed.
This includes electron-phonon scattering, photon emissions and even electron to electron interactivity. Moreover, the greater the number of qubits, which are necessary for Shor’s algorithm, the greater the decoherence.
Yet, although these may appear to be intractable problems inherent with quantum computing, there has been great progress in QEC methods. Case in point, Riverlane’s Deltaflow 2 method performs real-time QEC on up to 250 qubits. By 2026, this method should result in the first viable quantum application with million real-time quantum operations (MegaQuOp).
To break SHA-256 within one day, 13 million qubits would be needed, according to the AVS Quantum Science article published in January 2022. Although this would threaten Bitcoin wallets, many more qubits, at around 1 billion, would be needed to actually execute a 51% attack on Bitcoin mainnet.
When it comes to implementing the Grover algorithm, designed to leverage QC to search unstructured databases (unique hashes), a research paper published in 2018 suggested that no quantum computer would be able to implement it until 2028.
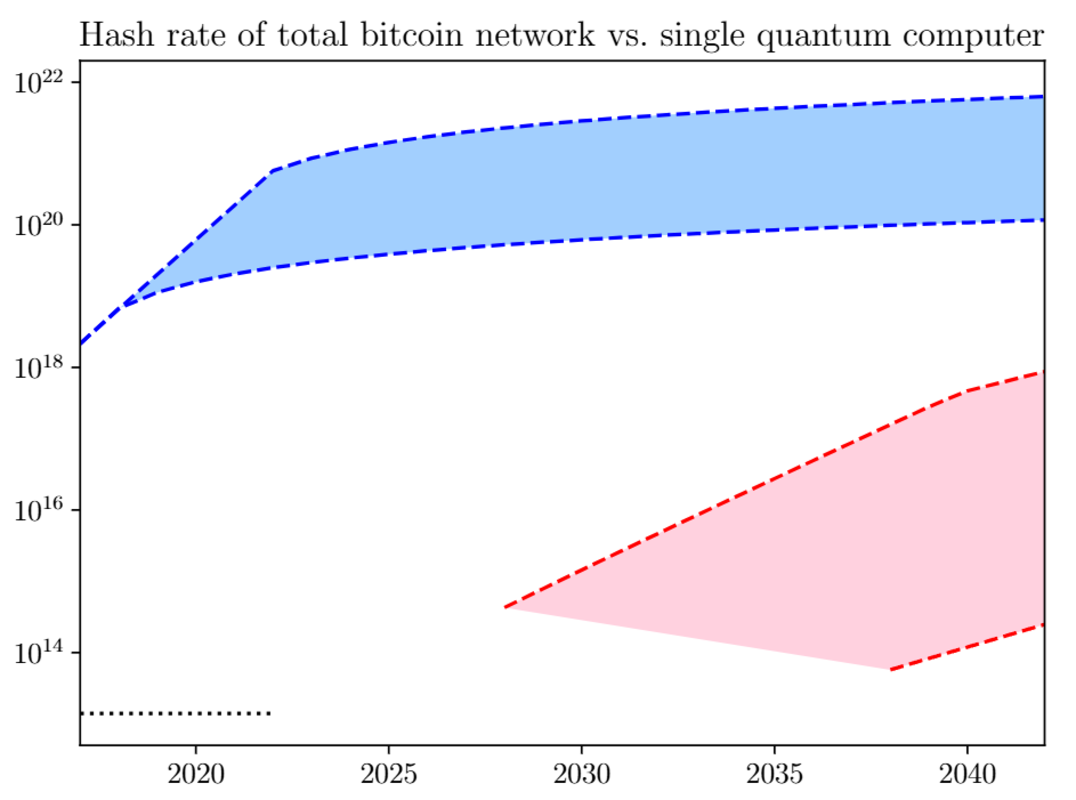
Image credit: Ledger Journal
Of course, Bitcoin network’s hashrate has greatly increased since then, and QC has to tackle decoherence as a major obstacle. But if QEC roadmaps eventually materialize into reliable quantum systems, what can be done to counteract the QC threat to Bitcoin?
Quantum Computing Resistance
There are multiple proposals to safeguard Bitcoin holders from quantum computers. Because a 51% QC attack is extremely improbable, the focus is mainly on hardening wallets. After all, if people cannot rely on their BTC holdings to be secure, this would cause an exodus from Bitcoin.
In turn, BTC price would plummet and the network’s hashrate would drastically decrease, making it far more vulnerable to QC than previously estimated. One such hardening is implementing Lamport signatures.
With Lamport signatures, a private key would be generated into pairs, 512 bitstrings from a 256-bit output. A public key would be generated with a cryptographic function to each of the 512 bitstrings. Each BTC transaction would need a one-time Lamport signature.
Because Lamport signatures do not rely on elliptic curves over finite fields in Elliptic Curve Digital Signature Algorithm (ECDSA), which is used by Bitcoin and can be exploited by Shar’s algorithm, but on hash functions, this makes them a viable quantum-resistant alternative.
The downside of Lamport signatures is their increased size, upward of 16KB, and one-time use. Of course, just by shifting addresses and keeping BTC in cold storage, thus avoiding private key exposure, can also prevent QC from being effective.
Another approach to confound potential QC attacks would be to implement lattice-based cryptography (LBC). Unlike in ECDSA, LBC avoids finite patterns by relying on discrete points in n-dimensional lattice (grid) space that extends infinitely in all directions. Because of this feature, there has yet been developed a quantum algorithm that could break LBC.
However, to implement a new type of cryptography, Bitcoin would have to undergo a hard fork. In that scenario, there would likely need to be many signals indicating that major breakthroughs in quantum computing, particularly in qubit count and fault tolerance, are imminent.
Bottom Line
It is safe to say that the Bitcoin mainnet itself is not in danger from quantum computing, in either the near or distant future. Yet, if QC were to compromise Bitcoin’s encryption—rendering SHA-256 and ECDSA obsolete—it would deeply impact confidence in the cryptocurrency.
This confidence is crucial, as demonstrated by major companies like Microsoft and PayPal, which have adopted Bitcoin payments, drawn by up to 80% savings compared to card transactions, zero chargebacks, and complete control over funds. With over 300 million holders globally, Bitcoin’s appeal as both a secure asset and a cost-effective payment option remains strong.
Ultimately, Bitcoin’s value is sustained by the capital and confidence behind it. Its historical volatility shows how events—ranging from Elon Musk’s tweets and PayPal’s integration to ETF launches and the FTX collapse—have impacted market sentiment. A fundamental threat to Bitcoin’s encryption could lead to panicked sell-offs, miner withdrawals, and a reduced mining difficulty, potentially opening the door to a 51% QC attack with fewer qubits.
To prevent such a scenario, Bitcoin holders and developers would do well to keep up with QC developments.
This is a guest post by Shane Neagle. Opinions expressed are entirely their own and do not necessarily reflect those of BTC Inc or Bitcoin Magazine.
[ad_2]

