[ad_1]
Bitcoin’s price is approaching major resistance zones while funding rates flip increasingly positive—an indication that long exposure is building up. But is this bullish pressure sustainable, or a sign of overheating?
Bitcoin’s (BTC) current price movement is testing a key area of resistance following a powerful rally, largely driven by a short squeeze. Now hovering just below $98,000, BTC is encountering strong supply at the confluence of the descending trendline, the 0.618 Fibonacci level, and the point of control from previous trading ranges.
At the same time, funding rates across major exchanges have turned positive, creating an important dynamic between derivatives and spot price action.
Key technical points
- Current Price: Bitcoin trades near $96,250 –$97,800, facing multiple resistance confluences.
- Funding Rates: Positive across major exchanges, reflecting increased long positions in perpetual futures.
- Price Structure: The short squeeze has lifted BTC into a range with previous bearish order blocks.
To better understand how this affects price action, it’s important to know what funding rates are. In perpetual futures markets, used heavily in crypto,funding is a periodic payment made between traders based on the difference between the futures and spot price.
When funding is positive, long traders pay short traders, which typically occurs when bullish sentiment dominates. When funding is negative, short traders pay longs, signaling bearish sentiment or aggressive shorting.
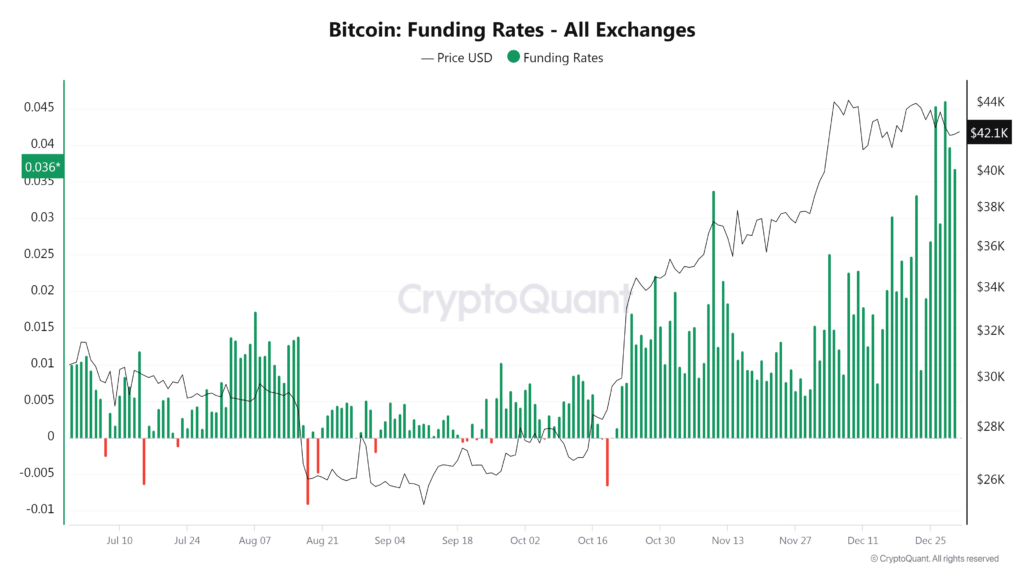
Bitcoin Exchange Funding Rate Source: CryptoQuant
Right now, Bitcoin’s positive funding rate suggests that traders are paying a premium to hold long positions. This often happens after a rapid rise, such as a short squeeze, when the majority of traders flip long expecting continuation. However, this can also set the stage for pullbacks if the market becomes overleveraged. If funding remains elevated without strong spot demand or volume, it raises the probability of a shakeout or local top.
You might also like: Lightchain AI highlights Cardano outshining BTC and Ether on ETF news
Market implications
The current resistance near $98,000 is a technically significant zone. It combines multiple macro-level resistance factors with a psychological milestone following a sudden squeeze. If BTC is able to consolidate above this area with volume and hold the breakout, the positive funding may fuel a continuation to $100,000 and beyond. However, failure to hold this level could trigger a rapid unwind of leveraged longs, reversing gains quickly.
Bitcoin’s funding rates remain a key metric to watch. As long as BTC consolidates above $96,200 with healthy volume, continuation is possible, but if positive funding persists without a breakout, a flush lower becomes more probable. Caution is warranted while BTC tests this pivotal level.
Read more: eToro eyes US IPO next week following Trump-induced volatility: report
[ad_2]

